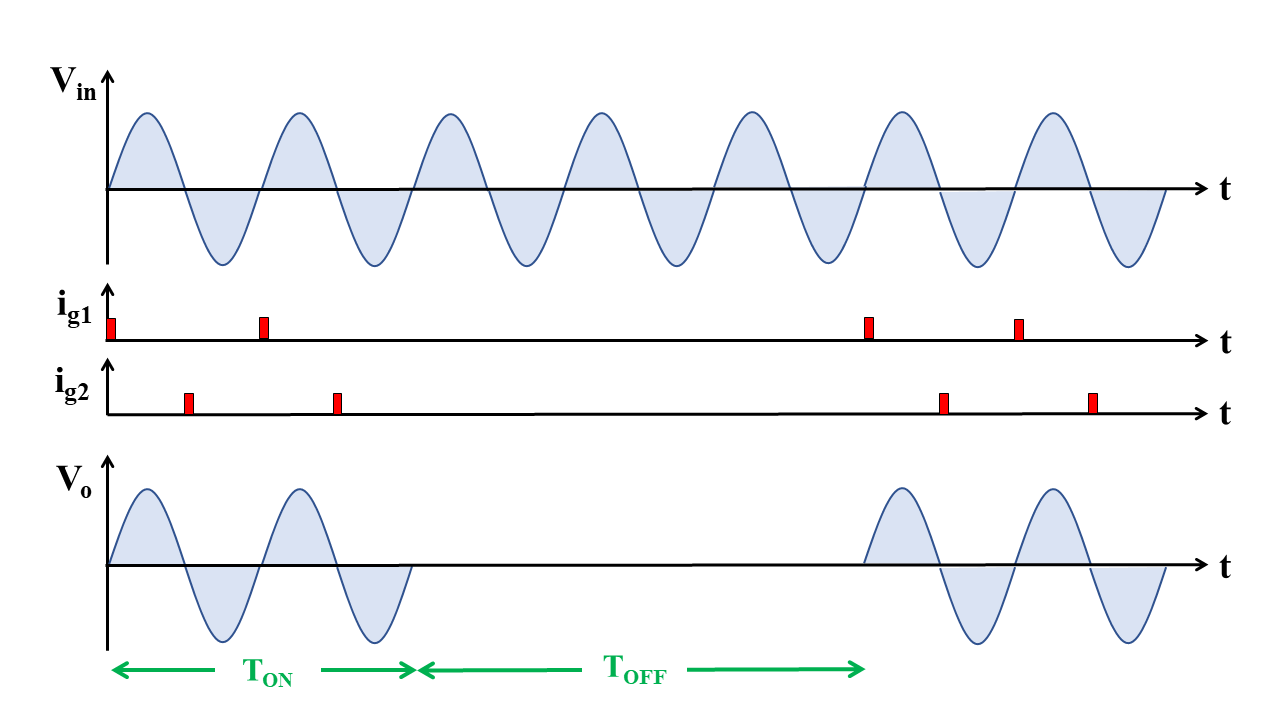
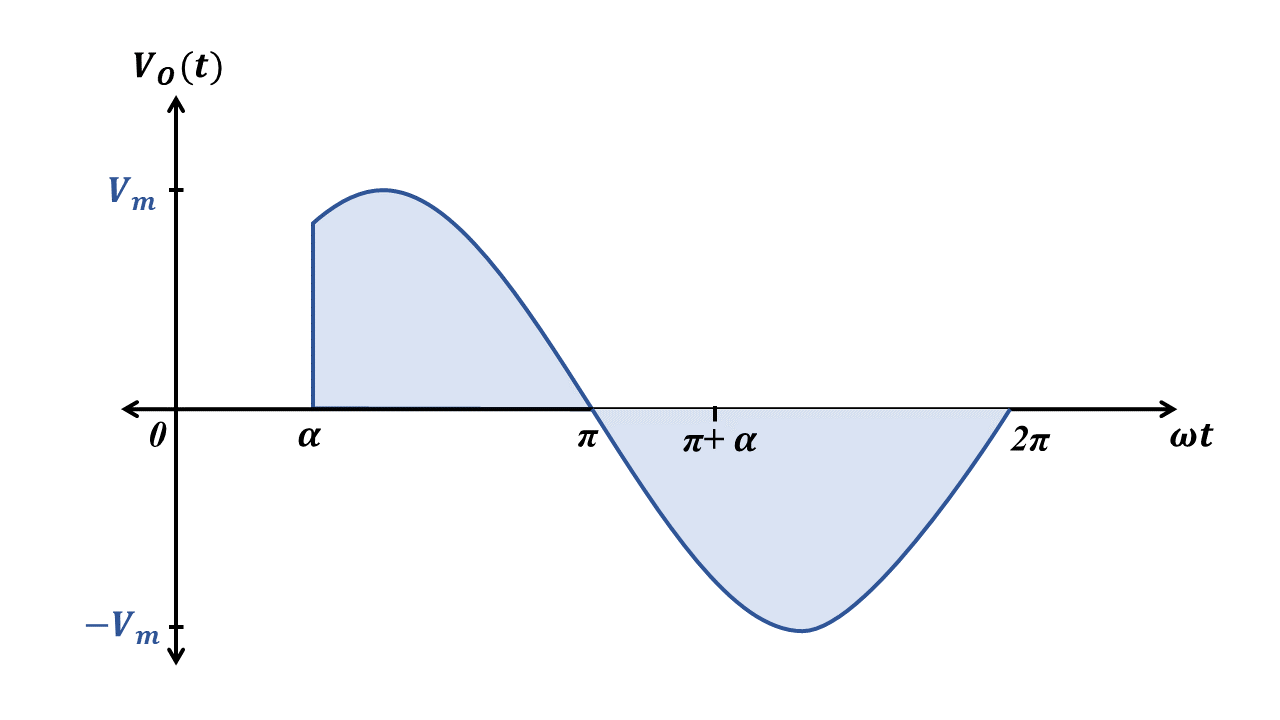
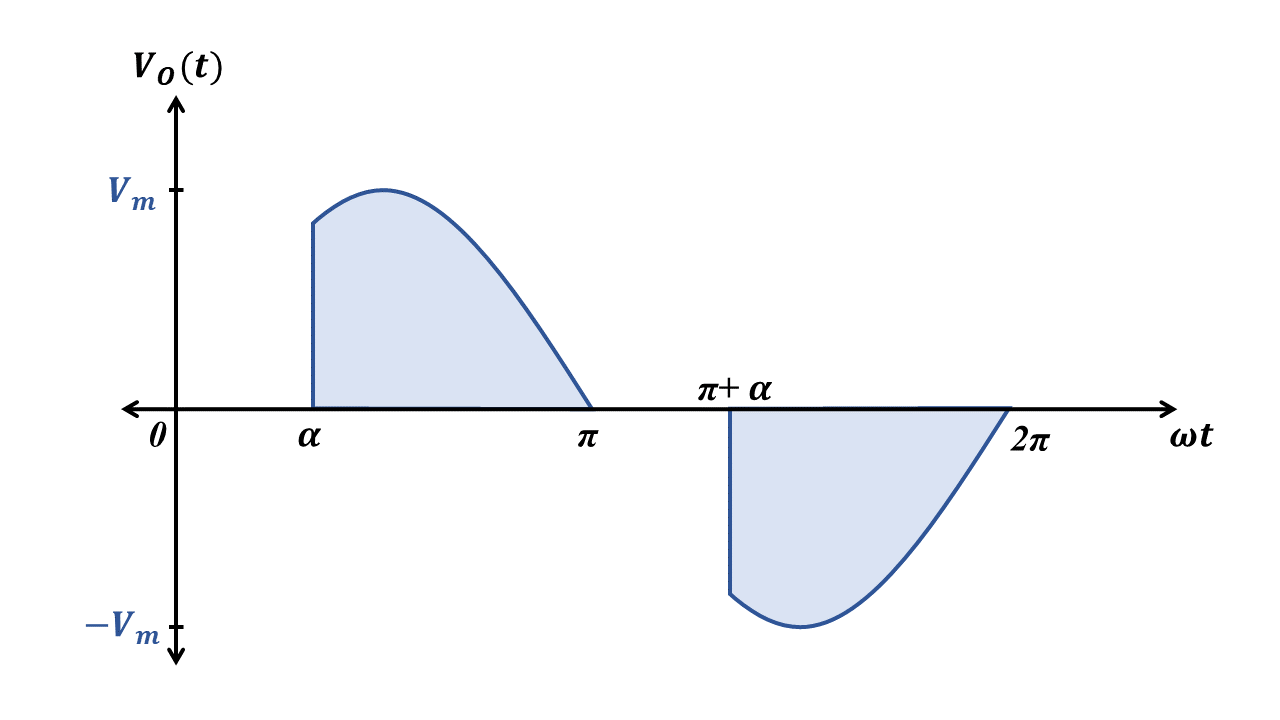
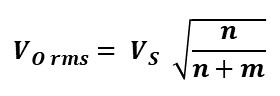Other possible configurations of AC voltage controllers
Note: The below are the other configurations of phase controlled full wave AC voltage controller.
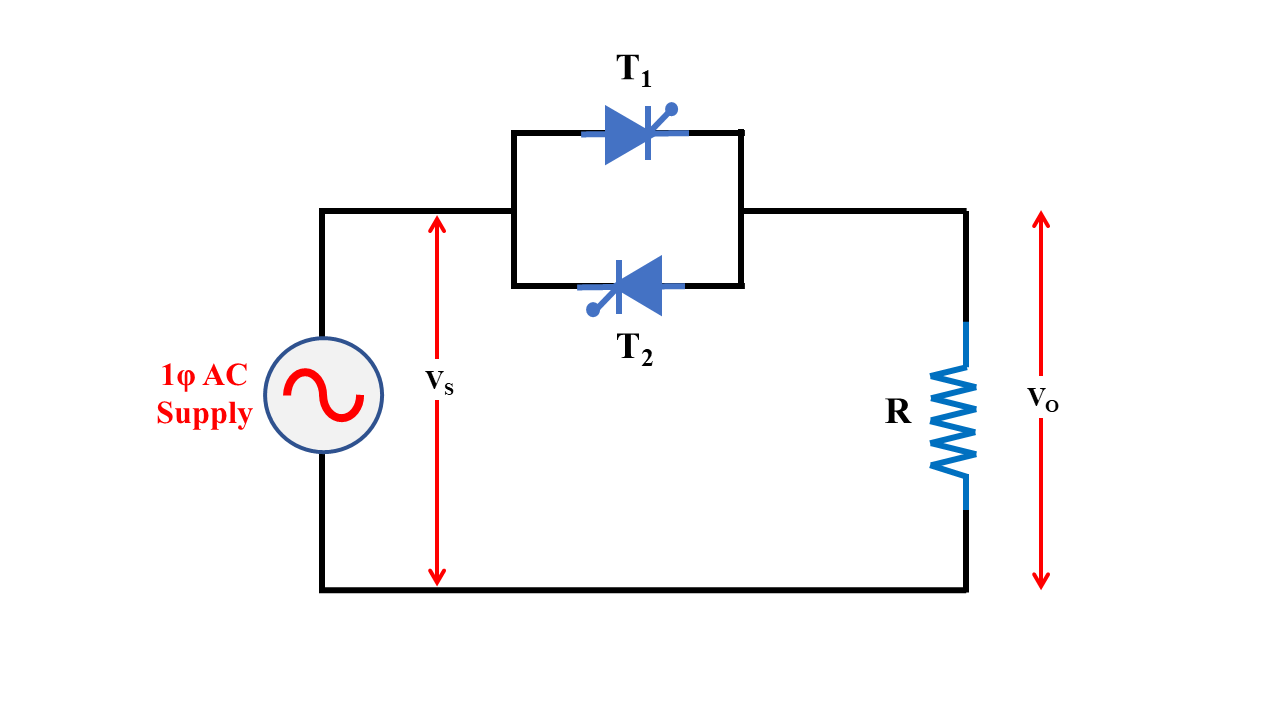
ACVR with Triac
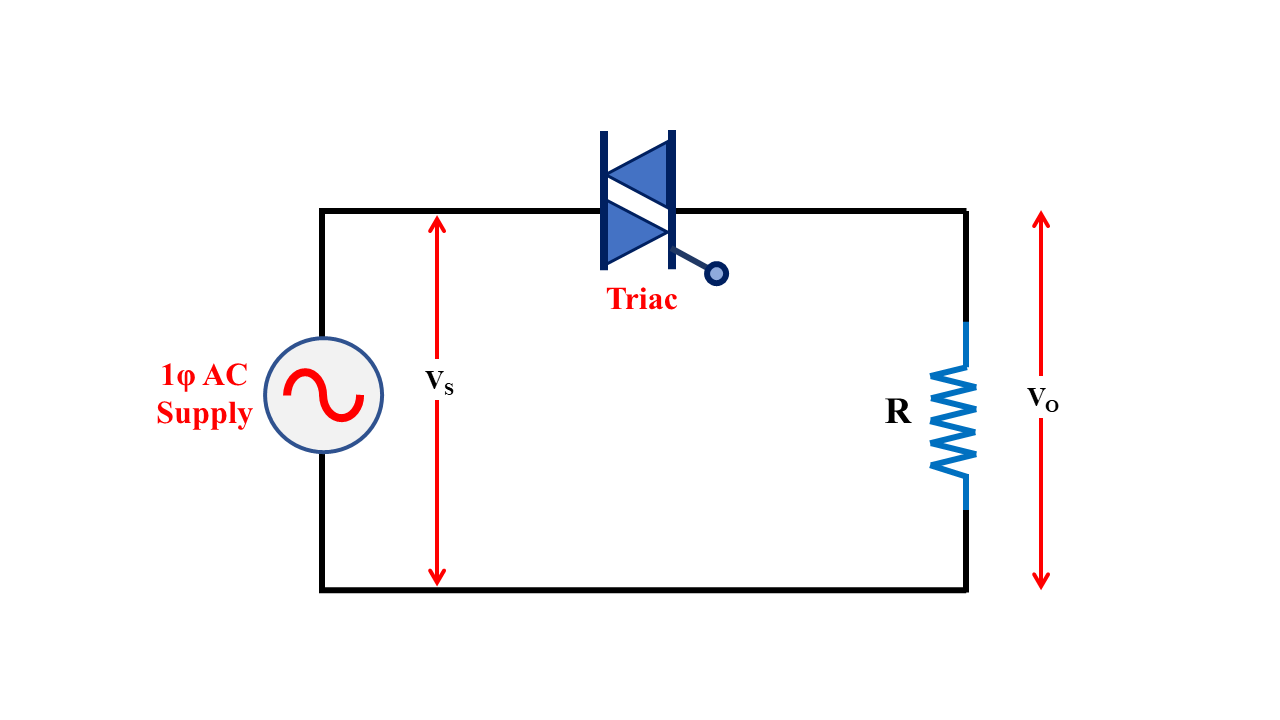
- This configuration is suitable for low-power applications where the load is resistive and has only a small inductance.
ACVR with only one SCR

- This configuration uses 4 power diodes and 1 SCR.
- In the positive half cycle, diodes D1, D3 and SCR T1 will conduct. During negative half cycle, diodes D2, D4 and SCR T1 will conduct.
- This configuration is cheaper as only one SCR is used (only one firing pulse circuitry is required)
- The disadvantage of this configuration is that, at any time, 3 devices (2 diodes and 1 SCR) will be conducting. This causes more voltage drop.